A Comprehensive Guide to Dementia Care
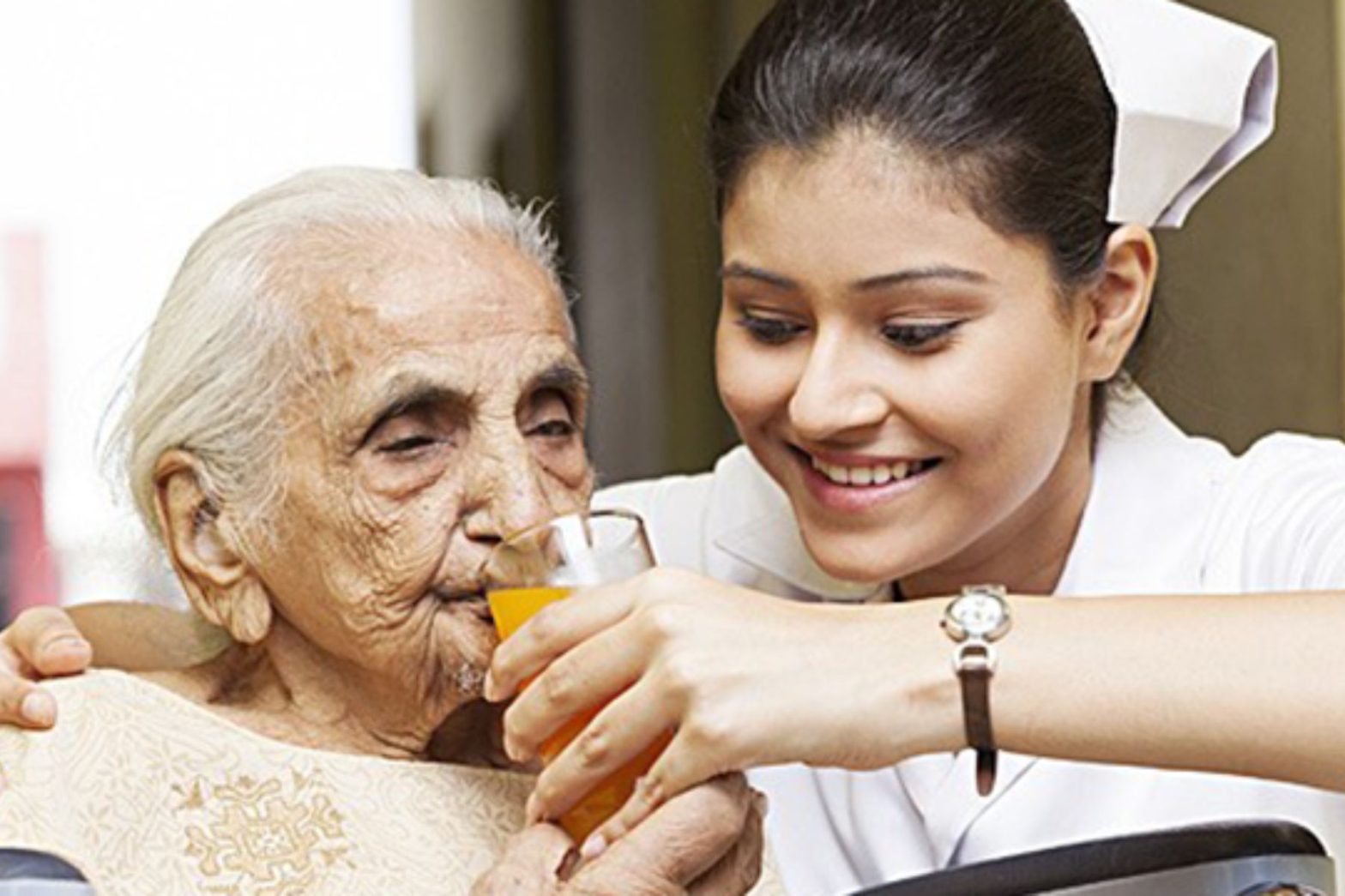
Dementia is a challenging and often misunderstood condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. As we witness an aging population, the need for effective dementia care is more critical than ever. In this blog, we’ll explore the nuances of dementia, and the impact it has on individuals and their families, and provide a comprehensive guide to compassionate and effective dementia care.
Understanding Dementia
Dementia is not a specific disease but rather a term used to describe a group of symptoms affecting memory, cognitive function, and daily activities. Alzheimer’s disease is the most common cause of dementia, but other conditions like vascular dementia, Lewy body dementia, and frontotemporal dementia also contribute to this complex landscape.
The Impact on Individuals and Families
Dementia not only challenges the cognitive abilities of those affected but also has profound emotional and practical implications for their families. Loved ones may struggle to cope with the changes in behavior, communication, and personality exhibited by the person with dementia. It is essential to approach dementia care with empathy, patience, and a commitment to preserving the dignity and quality of life of those affected.
Creating a Supportive Environment
Creating a supportive environment is a cornerstone of dementia care. This involves adapting living spaces to enhance safety, reducing unnecessary stimuli, and incorporating familiar objects to provide a sense of comfort. Establishing routines and maintaining consistency can help individuals with dementia feel more secure and oriented.
The benefits of training are numerous and vary depending on the type of training you pursue. Here are some overarching advantages:
Career Training
Enhanced Skills and Knowledge:
- Acquire specific skills and knowledge relevant to your chosen field.
- Stay updated on industry trends and advancements.
Career Advancement:
- Improve your career prospects and increase job opportunities.
- Enhance your competitiveness in the job market.
Personal Development:
- Foster personal growth and development.
- Build confidence in your abilities and expertise.
Networking Opportunities:
- Connect with professionals and peers in your industry.
- Expand your professional network for future collaborations.
Increased Earning Potential:
- Training often leads to increased earning potential.
- Certification and expertise can result in higher salaries.
Fitness Training
Professional Credibility:
- Gain recognition and credibility as a certified fitness professional.
- Attract more clients and opportunities.
Health and Wellness:
- Enhance your own health and wellness knowledge.
- Encourage a healthy lifestyle for yourself and others.
Job Satisfaction:
- Experience job satisfaction by helping others achieve their fitness goals.
- Enjoy a rewarding career in the fitness industry.
Varied Career Paths:
- Open doors to various fitness-related career paths.
- Explore roles as a personal trainer, group fitness instructor, or specialized fitness professional.
General Training
Skill Diversification:
- Diversify your skill set, making you more adaptable.
- Improve your problem-solving and critical-thinking abilities.
Personal Enrichment:
- Experience personal enrichment and a sense of accomplishment.
- Challenge yourself to learn and grow beyond your comfort zone.
Career Flexibility:
- Gain flexibility in career options.
- Many skills are transferable across different industries.
Stay Relevant:
- Stay relevant in a rapidly evolving job market.
- Demonstrate a commitment to lifelong learning.
Personal and Professional Growth:
- Boost your self-confidence and self-esteem.
- Foster continuous personal and professional growth.
Effective Communication Strategies
Communication becomes increasingly challenging as dementia progresses. Caregivers should prioritize clear and simple communication, using visual cues, gestures, and a calm, reassuring tone. Active listening and paying attention to non-verbal cues are crucial for understanding the needs and emotions of the person with dementia.
Promoting Meaningful Activities
Engaging in meaningful activities can significantly enhance the well-being of individuals with dementia. Tailoring activities to their interests and capabilities can provide a sense of purpose and accomplishment. Whether it’s enjoying music, art, or nature, finding activities that resonate with the person’s past interests can be enriching.
Caregiver Support and Well-being
Caring for someone with dementia can be emotionally and physically demanding. Caregivers must prioritize self-care to prevent burnout. Seeking support from friends, family, or support groups, and considering professional respite care can help maintain the caregiver’s well-being.
Navigating Dementia Care and Treatment Options
Regular medical check-ups are essential for individuals with dementia. Caregivers should work closely with healthcare professionals to manage symptoms, explore appropriate medications, and discuss potential treatment options. Staying informed about the latest advancements in dementia research can also aid in making informed decisions.
Dementia Care facts
- Definition: Dementia is not a specific disease but rather a term used to describe a group of symptoms affecting memory, cognitive function, and daily activities.
- Prevalence: Dementia is prevalent worldwide, with millions of individuals affected. Alzheimer’s disease is the most common cause, accounting for about 60-70% of cases.
- Symptoms: Common symptoms include memory loss, confusion, difficulty in problem-solving, language impairment, and changes in mood or behavior.
- Types: Dementia is not a singular condition; there are various types, including Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia, Lewy body dementia, and frontotemporal dementia.
- Risk Factors: Age is a significant risk factor, and the likelihood of developing dementia increases with age. Other risk factors include genetics, family history, cardiovascular health, and lifestyle choices.
- Global Impact: Dementia poses a substantial global health challenge. The number of people living with dementia is expected to rise as the world’s population ages.
- Diagnosis: Accurate diagnosis often involves a combination of medical history, cognitive assessments, laboratory tests, and sometimes neuroimaging studies.
- Treatment: While there is no cure for most types of dementia, certain medications may help manage symptoms and improve the quality of life for some individuals. Non-pharmacological interventions, such as cognitive stimulation and physical exercise, also play a crucial role.
- Impact on Families: Dementia not only affects the individual but also has a profound impact on their families and caregivers. The emotional, financial, and practical challenges can be overwhelming.
- Global Awareness: Increased awareness about dementia is essential for reducing stigma, promoting early diagnosis, and enhancing support for affected individuals and their families.
- Research and Progress: Ongoing research seeks to better understand the causes of dementia, develop effective treatments, and ultimately find a cure. Early detection and intervention are critical areas of focus.
- Community Support: Supportive communities and dementia-friendly initiatives help create environments that accommodate and understand the unique needs of individuals living with dementia.
Dementia care Conclusion
Dementia care requires a holistic and compassionate approach. By understanding the unique challenges individuals with dementia face and implementing effective strategies for communication, environment adaptation, and engagement, caregivers can make a significant positive impact. It is essential to view dementia care not only as a series of tasks but as a profound opportunity to enhance the quality of life for those navigating this complex journey.